BitMart is one of the most popular cryptocurrency exchanges in the world, offering various features such as Spot Trading, Futures Trading, staking, lending, and other investment programs. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of essential cryptocurrency terms on BitMart, helping you grasp and apply them in real-world trading.
Introduction to BitMart Exchange and the Importance of Terminology
In the volatile cryptocurrency market, BitMart stands out as a reputable exchange offering diverse services for investors. To trade effectively on BitMart, understanding specialized terminology is essential.
What is BitMart?
BitMart is a cryptocurrency exchange launched in 2017, headquartered in the Cayman Islands, supporting the buying and selling of over 1,000 cryptocurrencies. With a user-friendly interface, competitive trading fees, and various features, BitMart has attracted millions of users worldwide. Currently, the exchange operates in over 180 countries and ranks among the top exchanges in trading volume within the crypto industry.

Why is Understanding Cryptocurrency Terms Important?
Mastering specialized terms on BitMart not only helps you trade more efficiently but also provides several key benefits:
- Reduces risks caused by a lack of knowledge.
- Allows you to seize investment opportunities by understanding trading strategies.
- Helps you grasp how BitMart operates to optimize profits.
Basic Cryptocurrency Terms on BitMart
Understanding basic cryptocurrency terms on BitMart helps you trade more efficiently. Below are the most essential concepts every user should grasp.
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital asset that is encrypted and traded on blockchain technology. Unlike fiat currency controlled by central banks, cryptocurrency operates on a decentralized system, ensuring transparent and secure transactions without intermediaries.
Characteristics of Cryptocurrency:
- Decentralized: Not controlled by any organization or government.
- Highly Secure: Uses blockchain technology to store immutable data.
- Borderless Transactions: Enables fast, low-cost international transactions.
- Limited Supply: Most cryptocurrencies have a fixed supply, such as Bitcoin, which has a maximum of 21 million BTC.
Examples of Popular Cryptocurrencies:
- Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most valuable cryptocurrency.
- Ethereum (ETH): A blockchain supporting smart contracts.
- Binance Coin (BNB): The native coin of Binance, reducing transaction fees.
- Tether (USDT): A widely used stablecoin pegged to the USD.

Difference Between Coin and Token
One of the common confusions among new investors is distinguishing between coins and tokens.
Definition of Coin: A coin has its own blockchain, operates independently, and is mainly used for payments, storing value, or transaction fees.
Examples:
- Bitcoin (BTC): Runs on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Ethereum (ETH): Runs on the Ethereum blockchain.
- Binance Coin (BNB): Runs on the Binance Smart Chain (BSC).
Definition of Token: A token is a digital asset built on an existing blockchain and does not have its own blockchain.
Examples:
- USDT (Tether): Operates on multiple blockchains like Ethereum (ERC-20), BSC (BEP-20), TRON (TRC-20).
- Shiba Inu (SHIB): A meme token on Ethereum.
Note: Coins usually have higher value and recognition, while tokens offer creative applications in DeFi and NFT.

Cryptocurrency Wallets – Storage Solutions for Digital Assets
A cryptocurrency wallet is an essential tool for storing, sending, and receiving digital assets.
There are two main types of wallets:
Hot Wallet: Connected to the internet, allowing quick transactions. However, due to being online, it is more vulnerable to attacks and less secure.
- Examples: MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Binance Wallet.
Cold Wallet: Offline storage, ensuring higher security. Suitable for long-term storage to prevent hacking risks.
- Examples: Ledger Nano X, Trezor.
Tip: Use a hot wallet for frequent transactions and a cold wallet for long-term storage.
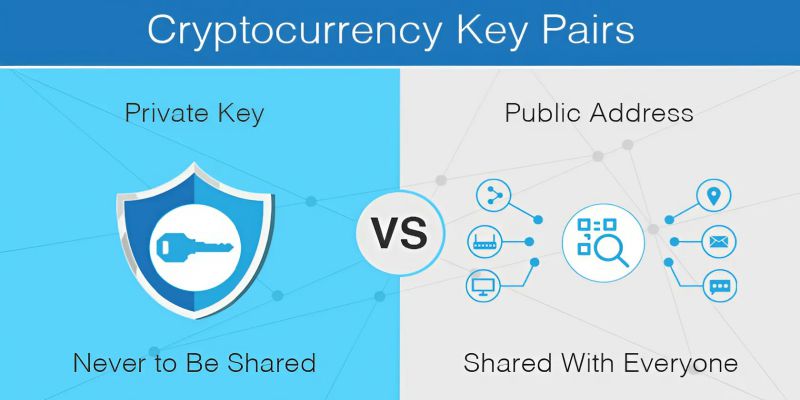
Public Key & Private Key
In cryptocurrency, public and private keys function like a bank account number and a password.
- Public Key: Similar to a bank account number, used to receive cryptocurrencies. It can be shared publicly without security concerns.
- Private Key: Similar to a bank password, used to access and manage wallet assets. Never share it, as anyone with access can control your funds.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that records transactions transparently and immutably.
How Blockchain Works:
- Each transaction is recorded in a block.
- Once full, a new block is created and linked to the previous one, forming a chain.
- The decentralized network ensures that no one can alter the transaction history.
Advantages of Blockchain:
- High Security: Transactions cannot be altered or forged.
- Transparency: All transactions can be verified on a blockchain explorer.
- No Intermediaries: Transactions occur directly between parties.
Gas Fee – A Crucial Factor in Transactions
Gas fee (transaction fee) is the cost you must pay when performing a transaction on a blockchain.
Factors Affecting Gas Fees:
- Blockchain Network: Ethereum usually has higher fees compared to Binance Smart Chain or TRON.
- Network Congestion: When many users transact simultaneously, gas fees increase.
- Transaction Type: Transferring USDT on Ethereum costs more than on TRON.
Trading Terms on BitMart
When trading cryptocurrency’s , you will encounter several important terms on BitMart related to buying and selling methods, order types, and trading mechanisms.
Spot Trading
- Buying/selling cryptocurrency instantly at the market price.
- You own the actual asset after the transaction.
- Lower risk, suitable for beginners.
Futures Trading
- Speculating on future prices without owning the asset.
- Can go Long (buy) or Short (sell).
- Supports leverage, but comes with higher risks.
Important Order Types
- Market Order: Executes immediately at the best available price.
- Limit Order: Executes when the price reaches your set level.
- Stop-Limit Order: Helps manage risk by setting a stop price.
Bid & Ask Prices
- Bid Price: The highest price a buyer is willing to pay.
- Ask Price: The lowest price a seller is willing to accept.
Liquidity
- Measures how easily an asset can be bought or sold without significantly impacting the market price.
Slippage
- The difference between the expected price and the actual executed price.
Margin Trading
- Leverage: Allows trading with a larger amount than your actual capital.
- Liquidation: Occurs when the asset value drops below the allowed threshold, leading to forced closure of positions.
Security & Risk-Related Terms You Need to Know
When trading cryptocurrencies, understanding security and risk-related terms on BitMart helps you avoid unnecessary dangers.
- KYC (Know Your Customer) – A mandatory identity verification process to comply with regulations and protect users from fraud.
- 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) – An additional security layer using authentication codes to reduce the risk of account breaches.
- Rug Pull – A common scam where project developers withdraw all funds and disappear, leaving investors with significant losses.
- Whale – Large investors holding massive amounts of cryptocurrency, capable of manipulating the market.
- Pump and Dump – A tactic where prices are artificially inflated using fake news, followed by a massive sell-off for profit, causing losses for retail investors.
- HODL – A long-term investment strategy that involves holding assets despite market fluctuations, waiting for value growth.

Terms Related to the BitMart Ecosystem
BitMart is not just a cryptocurrency exchange but also builds a comprehensive ecosystem to help users maximize their profits.
- BitMart Token (BMX) – The native token of the platform, offering benefits such as reduced trading fees and access to exclusive events.
- BitMart Earn – A financial service that allows users to earn interest on idle cryptocurrency through flexible savings programs.
- BitMart Staking – A method of locking assets to support blockchain networks and receive periodic rewards.
- BitMart Launchpad – A launch platform for new projects, providing early investment opportunities at discounted prices.
Conclusion
Mastering cryptocurrency terms on BitMart is the key to confidently trading and making effective investment decisions. Understanding these concepts will help you manage risks and maximize profits. The crypto market is constantly changing, but with solid knowledge and a well-planned strategy, you can seize opportunities and achieve success!