In the world of cryptocurrency, securing your assets is crucial. One of the most important elements of crypto security is the private key. Losing it can result in the permanent loss of your digital assets, while safeguarding it ensures full control over your funds. In this guide, we’ll explain what a private key is, how it works, how to obtain it, and explore the safest ways to store it.
What Is a Private Key?
A private key is a unique, randomly generated string of alphanumeric characters that acts as a secure digital password for your cryptocurrency wallet. This key gives you full control over your crypto assets, allowing you to authorize transactions and prove ownership of your funds. Without this key, you cannot access or manage the cryptocurrencies stored in your wallet.
A typical private key consists of 256 bits and is often represented in a 64-digit hexadecimal format. For example: E9873D79C6D87DC0FB6A5778633389F444FA073E6EF2B4F4B45F7D8E0234A9D1
Because of its complexity and length, the chances of someone guessing or cracking your key are virtually zero with today’s technology.

How Does a Private Key Work?
Private keys are a core part of how cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain networks. Here’s a simplified explanation of how they work:
- Key Pair Generation:
When you create a crypto wallet, it automatically generates two keys:- Private Key: Kept secret; used to authorize transactions.
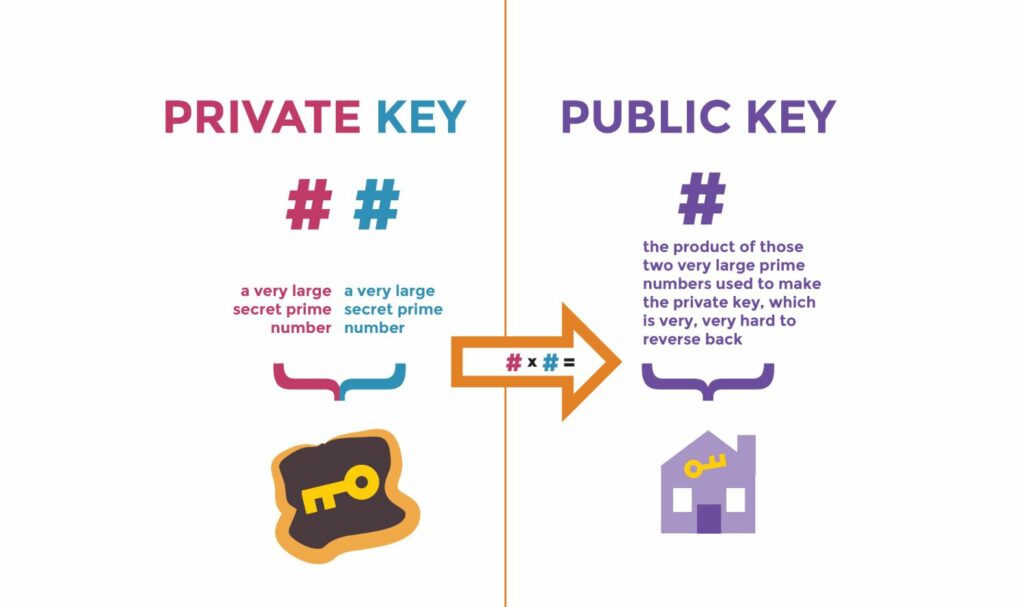
- Public Key: Derived from the private key; can be shared openly.
- Public Key and Address:
A public key is further hashed to create your wallet address (similar to a bank account number). This address is where others can send crypto to you. - Transaction Authorization:
When you initiate a transaction, your wallet software uses your key to create a digital signature. This signature verifies that you own the funds being sent. The transaction is then broadcast to the network, where miners or validators confirm it. - Security Through Encryption:
The process of generating a public key from a private key uses complex cryptographic algorithms, making it virtually impossible to reverse-engineer a private one from a public key.
Think of it like a secure mailbox system. The public key is the mailbox address where others can deliver messages (crypto), while the private key is the only key that can unlock and retrieve those messages.
Why Is a Private Key Important?
The importance of your private key cannot be overstated. Here’s why:
- Full Control: The private key is the only way to access and control your crypto funds. If someone gains access to your key, they can steal your assets.
- Security: Since cryptocurrencies are decentralized, there’s no central authority like a bank to recover your funds if your key is lost. Once a private key is compromised, the funds associated with it are at risk.
- Ownership Verification: It is crucial for proving ownership of crypto assets and authorizing transactions on the blockchain.
Losing your key means losing access to your funds forever. That’s why securely storing it is critical.
How to Get Your Private Key
When you create a cryptocurrency wallet, your private key is automatically generated by the wallet software. Depending on the type of wallet you use, you can view, back up, or even generate a blockchain private key QR code for easier access. Here are the main ways to obtain and secure your key based on your wallet type:
Software Wallets (Hot Wallets)
A software wallet is a digital wallet you can install on your phone, computer, or browser. It generates both a private key and a public key when you create a new wallet. Many software wallets offer access to the private key in the form of a recovery seed phrase (or backup phrase).
What is a recovery seed phrase?
The seed phrase is a series of 12 or 24 random words generated by the wallet. These words act as a backup for your key. If you lose access to your device, you can use this seed phrase to recover your wallet and funds.
How to manage your recovery phrase:
- Write down the seed phrase on paper and store it in a secure, private location.
- Avoid saving the phrase in digital formats (e.g., in cloud storage or on your phone), as these can be hacked.
- Do not share your seed phrase with anyone. If someone gains access to it, they can take control of your crypto assets.
Examples of software wallets:
- MetaMask (browser-based wallet)
- Trust Wallet (mobile wallet)
- Exodus (desktop and mobile wallet)
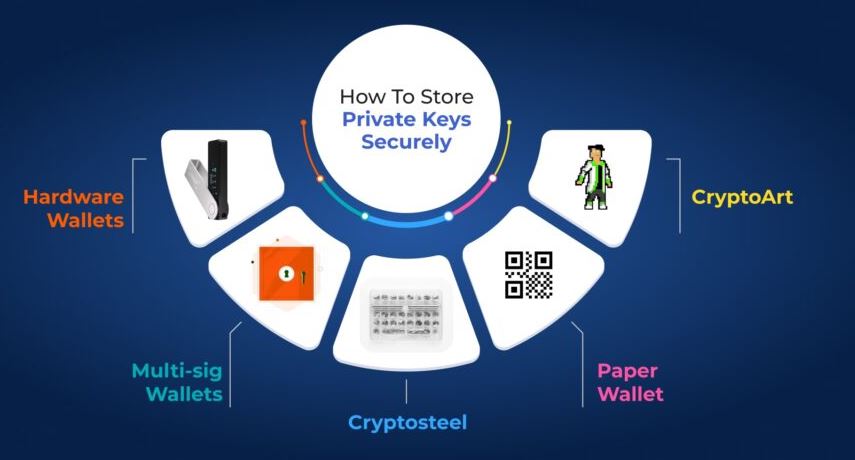
Hardware Wallets (Cold Wallets)
A hardware wallet is a physical device designed to store your private key offline. This makes it far more secure against cyber threats like hacking, phishing, and malware. Hardware wallets do not display your key unless you specifically request to view it, reducing the risk of accidental exposure.
How hardware wallets protect your key:
- The private key is encrypted and stored within the device.
- When you need to sign a transaction, the wallet processes the signature internally and sends it to the blockchain without exposing the key to the internet.
- You typically receive a recovery seed phrase when setting up the wallet, which serves as a backup in case the device is lost or damaged.
Examples of hardware wallets:
- Ledger Nano S / Ledger Nano X
- Trezor Model T
- SafePal S1
How to Safely Store Your Private Key
There are two main categories of private key storage: hot wallets and cold wallets. Each has its own advantages and risks.
Online Storage
Hot wallets are connected to the internet and include mobile apps, desktop applications, and web wallets. They offer convenience but are more vulnerable to hacking and malware attacks.
Tips for Securing a Hot Wallet:
- Use a reputable wallet provider with strong security features.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for added protection.
- Avoid storing large amounts of crypto in your hot wallets.
Offline Storage
Cold wallets store your key offline, making them more secure from cyberattacks. However, they require careful handling to avoid physical loss or damage.
Here are some popular cold storage methods:
Hardware Wallets
These are physical devices designed to securely store private keys offline. Hardware wallets are resistant to malware and cyberattacks, making them one of the safest storage options.
Paper Wallets
A paper wallet involves printing your private key on a physical piece of paper. While this method keeps your key offline, it is susceptible to physical damage, theft, or loss. To ensure durability, use high-quality paper and ink, and store the wallet in a safe location.
Encrypted USB Drives
You can store your key on an encrypted USB drive using software like VeraCrypt. Make sure the drive is kept in a secure location, such as a safe deposit box.
Cold Storage Devices
Some users create dedicated offline computers or devices to store private keys, ensuring they are never connected to the internet. This setup provides robust security but can be inconvenient for regular transactions.
FAQs
1. Is a Private Key the Same as a Password?
No, it isn’t. It functions similarly to a password in that it grants access to your crypto funds. However, it is much more secure due to its cryptographic properties.
2. Can I Recover a Lost Private Key?
If you lose your key and do not have a backup (such as a recovery phrase), you cannot recover your crypto assets. Always back up your key securely.
3. What’s the Difference Between a Public Key and a Private one?
- Private: Used to authorize transactions and prove ownership.
- Public: Derived from the private key and used to receive funds.
A private key is your gateway to controlling and securing your cryptocurrency. Understanding how it works and implementing proper storage practices are essential to protect your digital assets. By choosing secure methods like hardware wallets, paper wallets, or encrypted storage, you can minimize risks and maintain full control over your crypto investments. For more crypto security tips and updates, visit CryptoExlist.com regularly!